Evaluation of the Arsenic Extraction Capacity of Ricinus communis L.
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.28940/terra.v42i0.1836Keywords:
environmental contamination, phytoremediation, toxic elementsAbstract
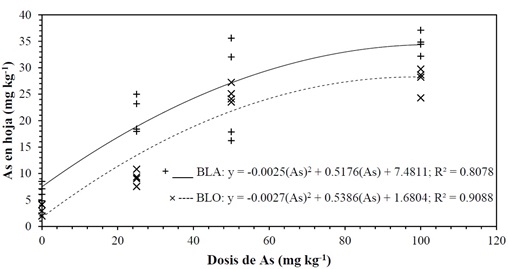
The castor plant (Ricinus communis L.) is a plant that has dif ferent benefits, such as the production of biodiesel and soil bioremediation. Due to the above, the castor plant’s ability to extract arsenic (As) was evaluated. For this, a randomized block experimental design with four repetitions was carried out. The evaluated treatments consisted of two types of biosolids (oxidation lagoon biosolids (BLO) and activated sludge biosolids (BLA) and four doses of As (0, 25, 50, 100 mg kg-1), under greenhouse conditions. As concentration was determined by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). From the quantification of As, the translocation factor (TF) and the bioaccumulation factor (FB) were estimated. The total nitrogen (N) content was quantified by the combustion method. Phosphorus (P) was analyzed by colorimetry using the metavanadate method, and the content of potassium (K), calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), copper (Cu), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe) and zinc (Zn) was quantified by atomic absorption. For percentage of oil The Soxhlet method was used in the seed. The plant height and the dry weight of biomass did not vary due to the treatment ef fect (P ≤ 0.05). The Translocation Factor (TF) and the Bioconcentration Factor (BCF) registered ranges of 0.20 - 0.63 and 0.28 - 0.75, respectively. The applied doses of As did not af fect the biomass and nutrient absorption in the castor plant, which indicates that this plant species is tolerant to toxicity with productive potential in soils contaminated with this element, in concentrations up to 100 mg kg-1.
Downloads
Publication Facts
Reviewer profiles N/A
Author statements
- Academic society
- Terra Latinoamericana
- Publisher
- Mexican Society of Soil Science, C.A.