Ef ficacy of Silicon Nanoparticles and Codasil® as Potential Biostimulants in Green Beans
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.28940/terra.v42i0.1885Keywords:
photosynthetic activity, nanotechnology, Phaseolus vulgaris L.Abstract
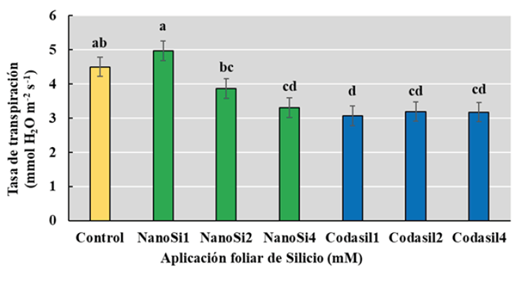
Global food demand has grown substantially due to population growth, where silicon (Si)-based biostimulants of fer a sustainable alternative for food production. Si plays an important role in mitigating abiotic stress. Therefore, innovative proposals for silicon supply have emerged in recent years, highlighting silicon nanoparticle application due to their physicochemical properties that facilitate plant absorption and have a biostimulatn function. Therefore, the objective of the present research is to evaluate the application ef ficacy of silicon nanoparticles and silico-based commercial product Codasil® as a potential biostimulant on biomass, yield, photosynthetic activity and transpiration rate in green beans. The study was conducted under shade net conditions in Delicias, Chihuahua, Mexico during August-October 2022 period. A completely randomized experimental design was used, with two silicon sources: silicon dioxide nanoparticles + KNO3 (NanoSi) and the commercial product Codasil® at doses of 0, 1, 2, and 4 mM, applied weekly via foliar application. The results obtained indicate that 1 mM silicon nanoparticle treatment improved total, yield and photosynthetic activity, while 4 mM Codasil reduced transpiration, increasing total biomass and yield. To conclude, foliar application of NanoSi at 1 mM and Codasil at 4 mM both work as biostimulants to improve green bean growth and yield.
Downloads
Publication Facts
Reviewer profiles N/A
Author statements
- Academic society
- Terra Latinoamericana
- Publisher
- Mexican Society of Soil Science, C.A.