Efecto Diferenciado del Silicio en la Interacción con NaCl en la Emergencia de Tres Variedades de (Solanum lycopersicum L.)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.28940/terra.v42i0.1927Palabras clave:
estrés salino, plántulas, tomateResumen
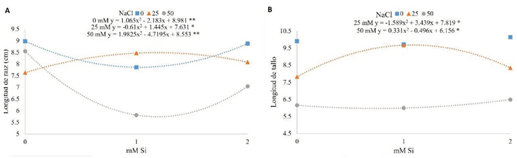
El estrés por salinidad es uno de los problemas ambientales con mayor impacto en la agricultura, ya que provoca cambios morfológicos, fisiológicos y genéticos en las plantas. Considerando el gran impacto de la salinidad, se buscan alternativas para mitigar el estrés en las plantas, en especial por cloruro de sodio (NaCl). Los productos a base de silicio (Si) tienen la capacidad de mejorar el crecimiento y desarrollo de las plantas, al estar expuestas en condiciones salinas. El objetivo de esta investigación fue evaluar la interacción NaCl-Si en la emergencia de plántulas de tres variedades de tomate. El diseño experimental fue completamente al azar con arreglo factorial de 32, donde el factor A fueron las concentraciones de cloruro de sodio (0 mM, 25 mM, 50 mM) y el factor B, las diluciones de Si (0 mM, 1 mM, 2 mM). Los resultados indican que las variedades de tomate fueron impactadas de diferente manera por la interacción NaCl-Si. En condiciones no salinas (0 mM de NaCl) el Si incrementó el crecimiento de tomate cherry y saladette, mientras que en condiciones de salinidad moderada (25 mM de NaCl) sólo el tomate saladette fue beneficiado.
Descargas
Publication Facts
Reviewer profiles N/D
Author statements
- Academic society
- Terra Latinoamericana