Banana Peels (Musa paradisiaca): Potential use as Biostimulant in Tomato Cultivation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.28940/terra.v42i.2015Keywords:
banana, metabolites, soil treatmentsAbstract
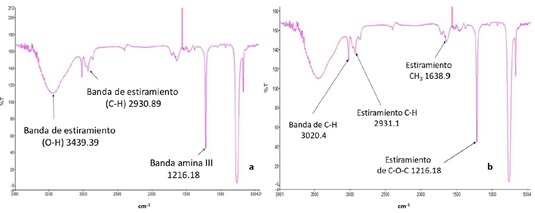
The progressive decrease in the quality of crops af fects their nutritional and economic values. Fertilizer with bio stimulant organic waste is gaining ground in technological research to amend soils and substrates, benefiting the growth and productivity of plants, thus it is important to analyze organic waste used for this purpose, to guarantee the use of its nutrients, converting waste into material profitable. This research seeks to analyze physical-chemical parameters of banana peels (Musa paradisiaca), to produce biofertilizers and/or bio stimulants usable in tomato crops (Solanum lycopersicum L.). The methodology includes cleaning and drying the shells, grinding and dividing the plant material into groups (I: Raw sample, II: Sample for ethanolic extraction, III: Sample for extraction with acetone, IV: Sample for extraction with petroleum ether). Functional groups of metabolites were determined in the extracts; the dried and pulverized raw sample was used to fertilize soils at dif ferent mass percentage, determining its quality with physical-chemical parameters before and af ter the process, the fertilized soil was used to determine the ef fect of the mixtures on a S. lycopersicum crop, measuring plant growth and productivity variables. The ethanolic extract is obtained with a higher percentage yield and presents a more varied matabolites profile, providing the crop soil with a significant improvement in most of the variables (micro and macronutrients), however, it causes a slight increase in pH and, despite obtaining a higher percentage of organic matter, the applied treatments do not improve the growth and productivity parameters of the tomato. The results allow establishing reference parameters related to the chemical composition of bio stimulants, and suggest furthering the use of other mixtures based on banana peels, to contribute to the reduction of the use of agrochemicals, of fering environmentally friendly alternatives.
Downloads
Publication Facts
Reviewer profiles N/A
Author statements
- Academic society
- Terra Latinoamericana
- Publisher
- Mexican Society of Soil Science, C.A.