Effect of Dif ferent Doses of NPK Fertilizer and Manure on N, P, K, Chlorophyll and Sweet Corn Yield in Vertisols
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.28940/terra.v42i.2028Keywords:
total-N, P-available, K-available, photosynthetic pigment, Zea mays saccharateAbstract
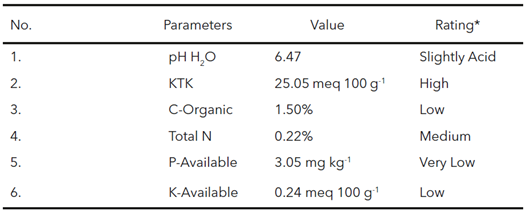
Vertisols is one of the soils with problems in nutrient availability, necessitating nutrient input in the form of fertilizer. The continuous use of inorganic fertilizers can negatively impact soil quality and the environment. Thus, it is essential to reduce their use and balance them with manure. This study aims to evaluate the ef fect of combining inorganic fertilizers with manure on improving the availability of Vertisols nutrients and the growth and yield of sweet corn (Zea mays saccharata). The research was conducted in Sidokerto, Plupuh, Sragen, from March 2023 to August 2023, using a Randomized Complete Block Design (RCBD) with 9 treatments and 3 replications. The treatments included a control (A), NPK recommendation (B), manure (C), and combinations of manure and inorganic fertilizer at predetermined doses. The observation variables were C-Organic, CEC, Total-N, P-Available, K-Available, chlorophyll, and the growth and yield of corn. The results showed that the application of ¾ NPK + 1500 kg ha-1 of manure increased N-Total by 38%, P-Available by 38.68%, K-Available by 57%, chlorophyll by 29%, plant height by 28.25%, number of leaves by 20%, stem diameter by 22.89%, cob weight by 31%, cob length by 48%, and cob diameter by 29% compared to the standard NPK treatment. Application of manure and inorganic fertilizers can increase the availability of N, P, K nutrients in Vertisols, growth, and yield of sweet corn.
Downloads
Publication Facts
Reviewer profiles N/A
Author statements
- Academic society
- Terra Latinoamericana
- Publisher
- Mexican Society of Soil Science, C.A.