Influence of Biofertilizers on the Development and Mineral Composition of Broccoli (Brassica oleracea var. italica)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.28940/terralatinoamericana.v43i.2227Keywords:
Bacillus spp., glucosinolates, vermicompost leachate, PGPRAbstract
This study aimed to evaluate the impact of dif ferent biofertilizers on broccoli cultivation during the autumn-winter 2022-2023 cycle in Saltillo, Coahuila, Mexico. Three combinations of Bacillus spp. and vermicompost leachate were tested using a randomized complete block design with four replicates, each consisting of five plants. The variables evaluated included fresh and dry biomass, stem diameter, inflorescence moisture, and the mineral content of macro- and micronutrients in the roots, inflorescence, and foliage, as well as glucosinolate concentration and chlorophyll estimation.
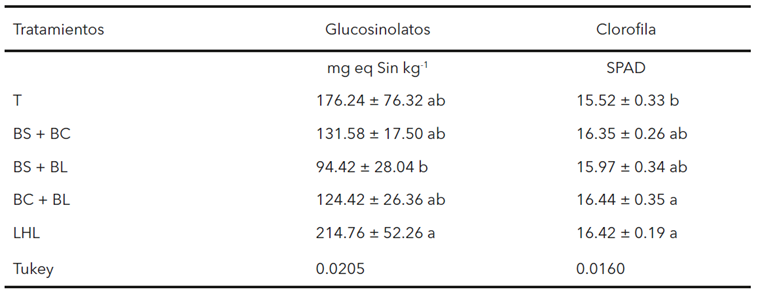
The application of biofertilizers significantly influenced inflorescence moisture and promoted nutrient accumulation, with notable dif ferences in nitrogen, phosphorus, calcium, and potassium. Moreover, the treatment with vermicompost leachate increased chlorophyll content, and high levels of glucosinolates were observed, although with considerable variability. These findings highlight the potential of biofertilizers as a viable alternative to improve the nutritional and functional quality of broccoli, particularly regarding nutrient accumulation and bioactive compound content, positioning them as a promising option to conventional fertilizers in sustainable agricultural systems.
Downloads
Publication Facts
Reviewer profiles N/A
Author statements
- Academic society
- Terra Latinoamericana
- Publisher
- Mexican Society of Soil Science, C.A.