Study of a Synthetic Surfactant in Sea Water Bioremediation and its Toxicity With Bioassays on Lettuce Seeds and Artemia salina
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.28940/terralatinoamericana.v43i.2170Keywords:
bioaugmentation, bioindicators, hydrocarbons, anionic surfactantAbstract
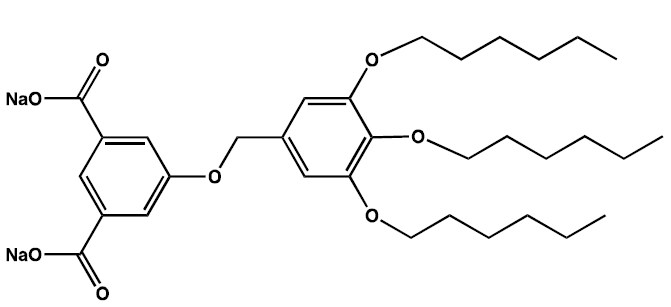
Oil pollution and its derivatives represent a serious environmental problem that requires ef fective remediation strategies such as bioremediation, a technology that has been widely studied and applied. This process employs microorganisms to degrade, transform, or reduce pollutants and their environmental impact. However, it faces challenges such as the low bioavailability of contaminant compounds. In this study, the bioremediation of synthetic seawater contaminated with total petroleum hydrocarbons (TPH) was evaluated using the bacteria Wautersia eutropha and Pseudomonas aeruginosa in combination with the synthetic anionic surfactant 5-(3,4,5-trishexyloxy)benzyloxy disodium isophthalate (AS-5) at a concentration of 200 mg L-¹. The results showed TPH degradation rates of 85.3% with P. aeruginosa, 78.5% with W. eutropha, and 85.9% with both strains combined. In the AS-5 bioassays, the median lethal concentration (LC50) was 586.33 mg L-¹ for Artemia salina and
1100 mg L-¹ for Lactuca sativa L. Furthermore, the integral phytotoxicity index (IPI) was determined in lettuce seeds at concentrations of 50, 100, and 200 mg L–1 of AS-5, yielding values of 11.6, 29.0, and 38.1%, respectively. The most af fected parameter was hypocotyl elongation.
Downloads
Publication Facts
Reviewer profiles N/A
Author statements
- Academic society
- Terra Latinoamericana
- Publisher
- Mexican Society of Soil Science, C.A.