Richness of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi Associated With Forest Species in the Southeast of the State of Campeche, Mexico
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.28940/terra.v43i.2031Keywords:
biofertilizers, endomycorrhizae, spores, nodulationAbstract
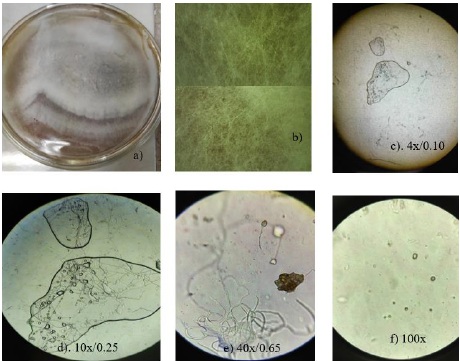
Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) are symbiotic associations of soil and plant roots. They are an alternative for biofertilization, biocontrol and bioremediation agents in production systems. The work consisted of morphologically characterizing the richness and efficiency of HMA in different types of vegetation: medium evergreen forest (SMP), agroforestry system (SAF) and milpa system intercropped with fruit trees (MIAF). In each type of vegetation, the roots of forest species of economic interest for the Programa Sembrando Vida (PSV) were obtained. The root samples were transported to the analysis and biotechnology laboratories of TECNM, Escárcega and Chiná campuses, Campeche, subjected to the sieving and decantation method to isolate spores. Three enriched media were used to evaluate the growth of AMF. Efficiency was validated by root growth and its relationship with mycorrhizal nodulation using different methodologies. Four AMF of the order Glomerales obtained from roots of forest species in SMP were characterized [(Astronium graveolens Jacq. (jobillo), Lonchocarpus castilloi Standl. (machiche), Swietenia macrophylla King (mahogany), Manilkara zapota L. (chicozapote) and Pimienta dioica L. (black pepper)]. The growth and reproduction of AMF in the laboratory was better using the Sabouraud enriched medium, which demonstrated significant results when applied in an 80/20 ratio in SAF and MIAF species. Regarding growth and nodulation efficiency in species such as Cedrela odorata L. (red cedar), Caesalpinia platyloba S. Watt (chakté-viga) and Cordia dodecandra A.D.C. (ciricote), and species in fast-growing crops such as
Zea mays L. (corn) and Pachyrhizus erosus L. Urban (jicama), they showed significant differences between treatments, according to the one-factor analysis of variance. In conclusion, HMA are a good option as a biofertilizer in fast-growing and forest species, facilitating the absorption and transport of nutrients and water.
Downloads
Publication Facts
Reviewer profiles N/A
Author statements
- Academic society
- Terra Latinoamericana
- Publisher
- Mexican Society of Soil Science, C.A.