Materia Sedimentable de la Laguna de Oxidación de Parcona Como Enmienda para Suelos Semiáridos de Ica–Perú
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.28940/terralatinoamericana.v43i.2161Palabras clave:
economía circular, abono, propiedad físico-química, sedimentosResumen
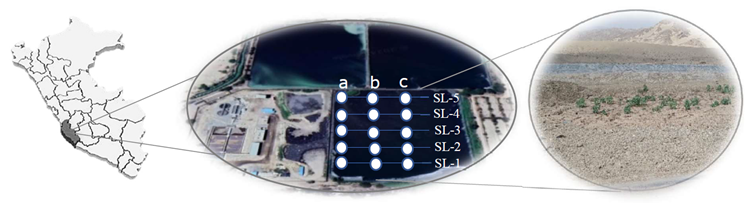
El tratamiento de aguas residuales en lagunas de oxidación consiste en la depuración del agua, aunque ignora la reutilización de los sedimentos acumulados. El objetivo del estudio fue describir la materia sedimentable de la laguna de oxidación de Parcona y valor para el suelo semidesértico de Ica, Perú. Se usó un diseño descriptivo en la laguna de oxidación, donde se establecieron cinco líneas de muestreo (LM-1, LM-2, LM-3, LM-4 y LM-5). En cada una de las líneas, se recolectaron tres muestras de materia sedimentaria y, luego, se mezclaron para formar una muestra volumen que se analizó por duplicado para determinar el pH, materia orgánica, textura, nitrógeno y fósforo. Los principales resultados señalaron que el pH estuvo en el rango neutro (6.6-7.3). La materia orgánica varió de rango medio a muy alto (2.21%-13.87%). La textura indicó altos contenidos de arcilla en la LM-1 (11.3 g cm-³) y LM-2 (12.3 g cm-³), mientras que LM-3 (73.8 g cm-³) y LM-4 (65.8) tuvieron mayor limo. Los niveles de nitrógeno fueron elevados en LM-2 (1092 mg kg-1) y LM-3 (1321 mg kg-1), y el fósforo fue alto en todas las líneas de muestreo. Se desconoció la variabilidad físico-química de la carga sedimentaria como proceso complejo de sedimentación. El hallazgo descrito presenta como valor primario el potencial de este biosólido como fertilizante agrícola, pero las diferencias en pH, materia orgánica y textura requieren una gestión cuidadosa para evitar efectos adversos en suelos agrícolas. La materia sedimentable de la laguna de oxidación mostró propiedades nutritivas aprovechables, destacando su valor como fertilizante en suelos semidesérticos dentro de una economía circular.
Descargas
Publication Facts
Reviewer profiles N/D
Author statements
- Academic society
- Terra Latinoamericana